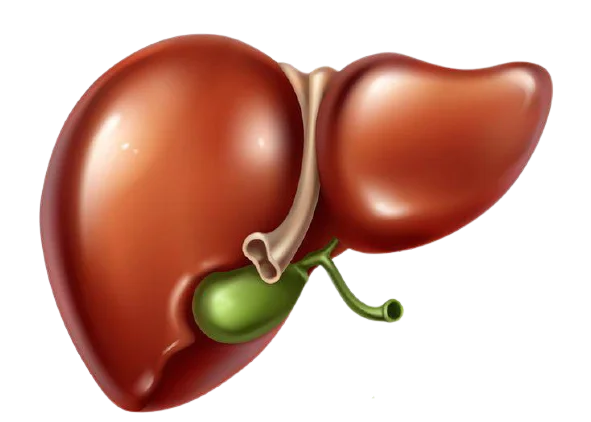
Understanding the Liver
AUTOIMMUNE HEPATITIS
Autoimmune disease occurs when the body’s immune system attacks liver cells causing the liver to get inflamed. The immune system normally protects people from infection by identifying and destroying bacteria, viruses, and other potentially harmful foreign substances.
LIVER TRANSPLANATION
Liver transplantation also may be used to rescue patients who present with fulminant hepatic failure secondary to autoimmune hepatitis.
SINGS AND SYMPTOMS
Autoimmune hepatitis may present as acute or chronic hepatitis or as well-established cirrhosis, although in rare cases it presents as fulminant hepatic failure.
DIAGNOSIS
This is usually made by taking a careful look at the medical history, performing a physical examination and also doing a liver biopsy.
TREATMENT
For a long period of time, corticosteroids, either alone or in combination with azathioprine, have been the mainstays of drug therapy for patients with autoimmune hepatitis.